What is spread in Forex? It’s a question both beginners and advanced traders often ask. Spread plays a pivotal role in trading, influencing decisions and profitability. In this article, you will learn what spread in Forex truly means, how it’s calculated, its significance to traders, the different types of spreads, how to reduce spread loss, etc.
Table of contents:
2. How to Calculate Spread in Forex?
3. Why do Spreads Matter to Traders?
4. 5 Ways to Minimise Spread Loss in Forex
5. Spread in 3 Different Forex Pairs
6. 5 Factors Influencing the Spread
8. Looking for Forex Brokers with Low Spreads?
From Spread Theory to Action: Explore with Our Demo Account
What is Spread in Forex?
In Forex trading, the term “spread” is often mentioned, but what exactly does it mean? At its core, the spread is the cost a trader pays to trade the Forex markets. Specifically, it’s the difference between a currency pair’s buying (Bid) and selling (Ask) price.
Imagine walking into a currency exchange booth. You’ll notice two prices listed for every currency: one price if you want to buy the currency and another price if you want to sell it. The difference in prices is essentially the spread, and it’s how the currency exchange market operators make a profit.
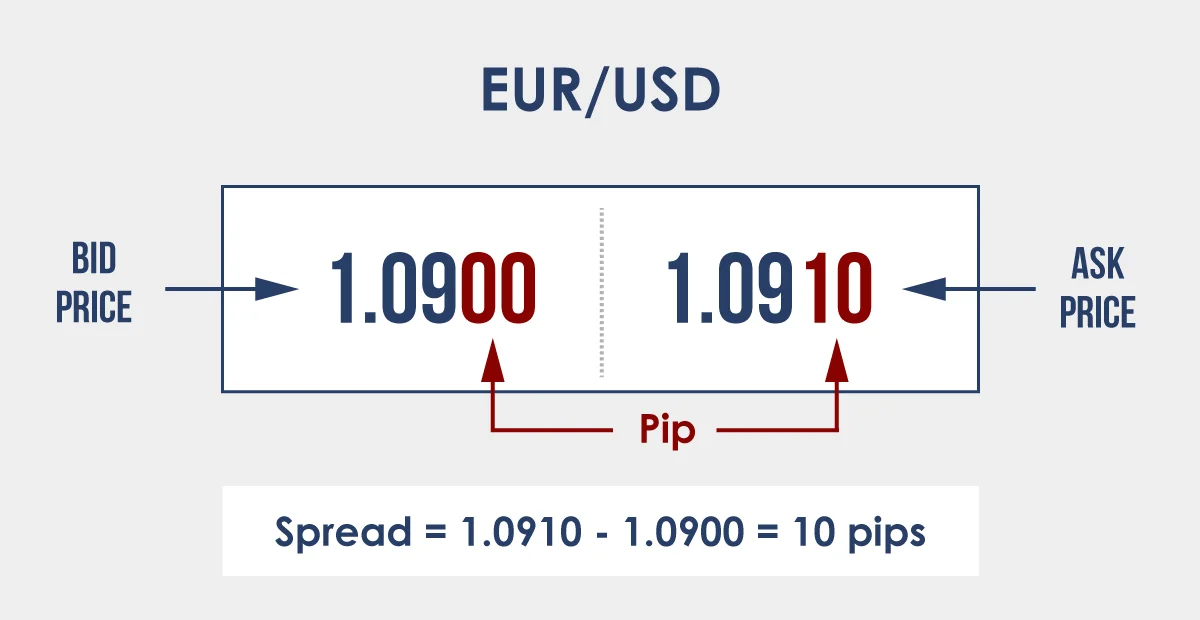
Example:
Let’s say you’re travelling to US and need to exchange your Euros for US dollars. At the exchange booth, the board displays:
EUR to USD: 1.0900 (Bid)
EUR to USD: 1.0910 (Ask)
If you were to buy US dollar, you’d get 1.0900 US dollars for every Euro. However, if you decided to exchange those US dollars back for Euro immediately, they’d use the sell rate of 1.0910. The difference, of 0.001 in this case, is the spread, which the exchange keeps as their fee.
In the Forex market, this spread is typically measured in “pips.” Using the above example, the spread would be 10 pips. Learn more about what is pip in forex .
Figures:
In Forex trading, major currency pairs like the EUR/USD, GBP/USD, and USD/JPY often have tighter spreads than minor or exotic pairs. For instance:
The EUR/USD might have a spread of 0.8 pips.
Meanwhile, the GBP/JPY, being a more volatile pair, might have a spread of 3.5 pips.
Find out the 10 most traded currencies in the Forex market .
How to Calculate Spread in Forex?
Understanding how to calculate the spread in Forex is crucial for every trader, as it directly impacts the cost of a trade. The spread is the difference between the Bid (buy) and Ask (sell) prices of a currency pair.
Formula:
Spread = Ask Price – Bid Price
This difference is typically measured in “pips,” which is the smallest price movement in Forex and represents a fraction of the currency’s value. For most currency pairs, a pip is equivalent to 0.0001.
Example:
Imagine you’re looking at the trading platform for the EUR/USD currency pair. You observe the following:
Bid Price: 1.1200
Ask Price: 1.1205
To Calculate the Spread:
Spread = 1.1205 – 1.1200
Spread = 0.0005 or 5 pips
In this scenario, if you decide to enter a trade immediately, you’ll start with a 5-pip deficit, which represents the broker’s fee for facilitating the trade.
Wide Spread vs Tight Spread
Aspect | Wide Spread | Tight Spread |
Definition | A difference of, typically, 5 pips or more between the bid and ask price. | A difference of, typically, 0.1 to 1 pip between the bid and ask price. |
Typically Found In | Less liquid markets, exotic currency pairs, and times of high volatility. | Highly liquid markets, major currency pairs, competitive broker offerings. |
Implications for Traders | Higher trading costs and the potential for slippage might be less favourable for scalping . | Lower trading costs, more predictable entry and exit points, favourable for frequent trading. |
Examples | Found in exotic pairs like the USD/ZAR, EUR/TRY or during geopolitical events or major announcements. | Found in major pairs like the EUR/USD and GBP/USD or during peak trading hours in major markets. |
Best Suited For | Traders with a higher risk tolerance or those trading less frequently. | Day traders, scalpers, and those trading frequently or in large volumes. |
Why do Spreads Matter to Traders?
It is crucial for anyone involved in Forex trading to understand the significance of the spread. The spread directly impacts the cost paid by a trader when entering and exiting a trade. Therefore, it plays a crucial role in determining the profitability of each trade.
Cost Implications:
Every time a trader enters a position, they start at a slight disadvantage equal to the spread. Therefore, this means that the market needs to move in the trader’s favour by the amount of the spread for the trade to break even. The larger the spread, the more significant the initial disadvantage.
Trading Frequency:
For day traders and scalpers who enter multiple positions throughout the day, even a slightly larger spread can accumulate to a substantial cost. On the other hand, long-term traders who hold positions for days or weeks might be less affected by the spread. Learn more about day trading strategies .
Example:
Imagine a day trader who trades the EUR/USD pair 20 times daily. If the spread is 1 pip, and they trade 1 standard lot each time, the cost in terms of the spread would be:
20 trades x 1 pip x $10 (value of 1 pip for 1 standard lot of the EUR/USD) = $200 daily
Over a month, this amounts to $4,000 (considering 20 trading days), highlighting how even a small spread can have a significant impact over time. Learn what lot size is in forex.
Figures:
Consider 2 traders:
Trader A uses a broker with a spread of 0.5 pips for the EUR/USD.
Trader B uses a broker with a spread of 2 pips for the same pair.
If both traders make the same trades over time, Trader B’s costs will be significantly higher, affecting their overall profitability. Learn how to become a trader.
5 Ways to Minimise Spread Loss in Forex
Successfully navigating spreads is crucial for maximizing profitability in Forex trading. By understanding and implementing specific strategies, traders can minimize the impact of spreads on their trades and enhance their overall trading performance.
Trade During Peak Times:
Spreads are generally tighter during the 3 main trading sessions when liquidity is high. By trading during these times, traders can benefit from lower costs.
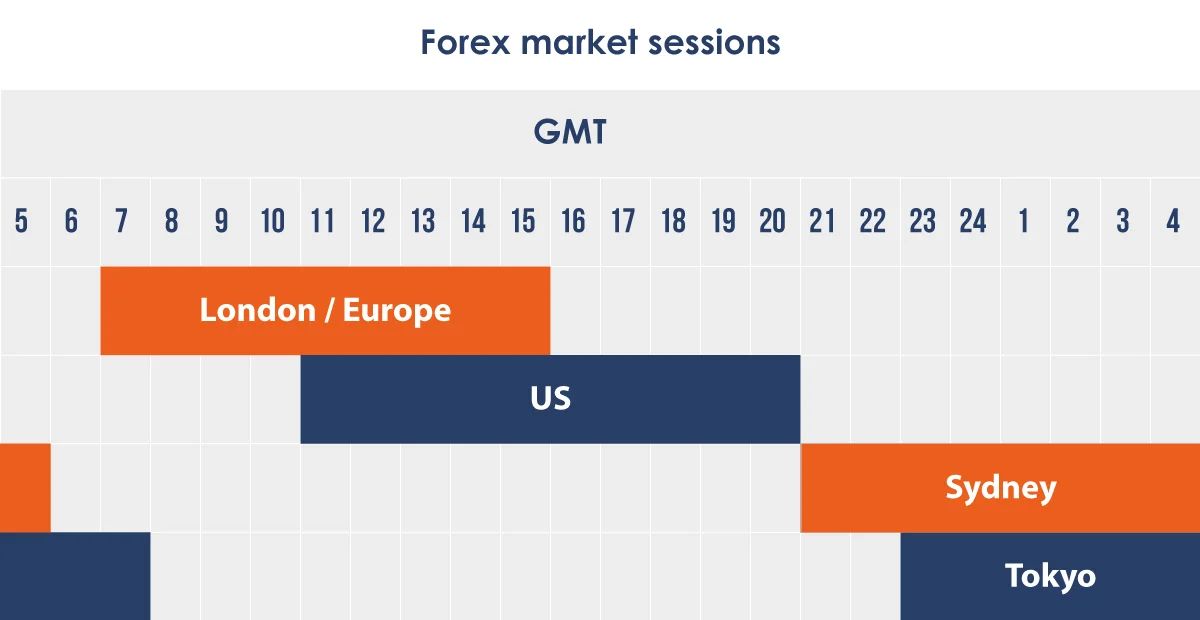
Example: The overlap of the London and New York sessions sees the highest trading volume, often resulting in tighter spreads for pairs like the EUR/USD, which might have a spread of 0.8 pips compared to 1.5 pips during the Asian session.
Factor in Spread Costs to Profit Targets:
Always consider the spread when setting profit targets. If the spread is wide, you might need a larger price move to achieve your profit target.
Example: If you’re scalping and aiming for a 10-pip profit on a pair with a 2-pip spread, the market needs to move 12 pips in your favour for you to achieve your net profit target. Find out if forex trading is profitable .
Avoid Trading Immediately Before/After Major News Releases:
Spreads can widen significantly during major economic announcements due to increased volatility. It is best to avoid trading during such events, especially if you are not an experienced trader.
Example: If you’re trading the GBP/USD pair, and there’s an upcoming Bank of England interest rate decision, the spread might jump from 1 pip to 5 pips around the news release.
Use Limit Orders:
Limit orders allow you to set a specific entry price, ensuring you don’t enter a trade if the spread is too wide.
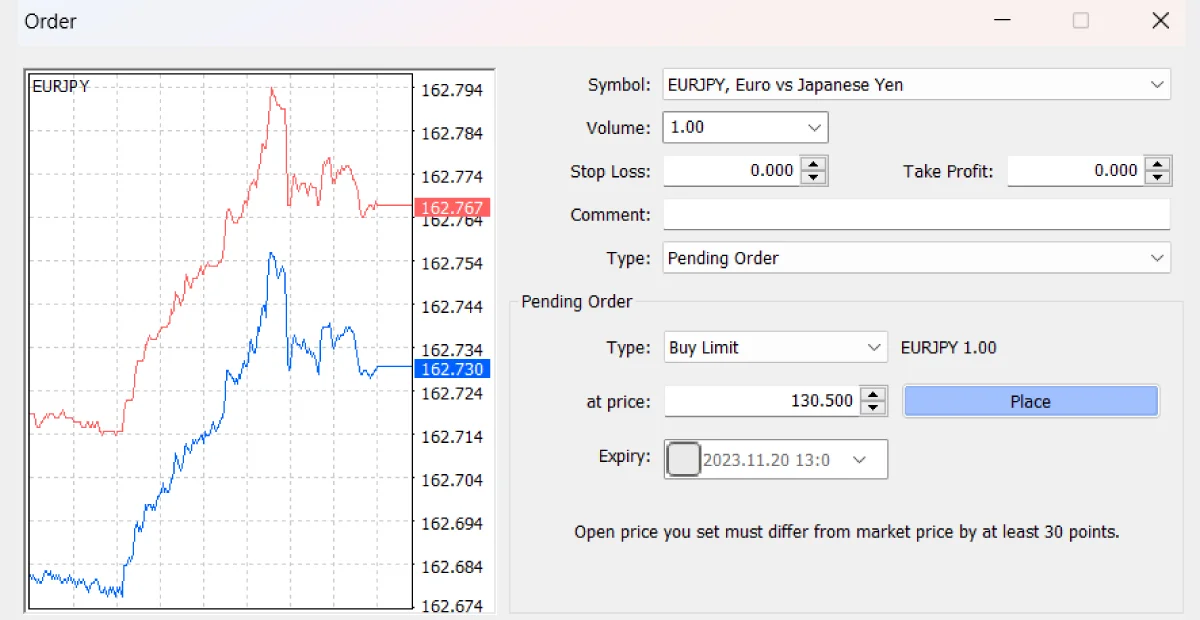
Example: If you set a limit order to buy EUR/JPY at 130.50, the order will only be executed if the Ask price (for buy orders) reaches that level, ensuring you don’t pay a higher spread.
Choose Your Currency Pairs Wisely:
Some currency pairs inherently have wider spreads. Being selective about which pairs to trade can help in managing spread costs.
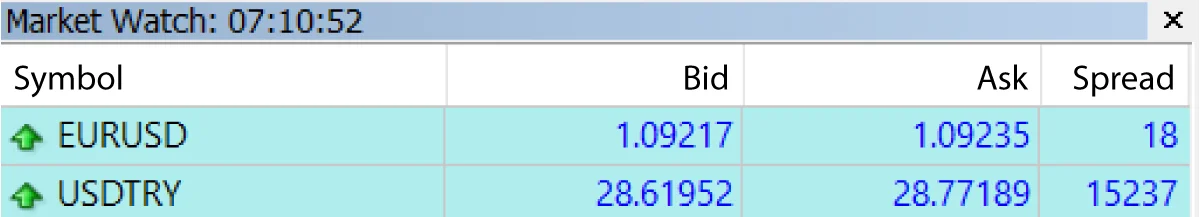
Example: If you’re a day trader, focusing on major pairs like the EUR/USD with tighter spreads can be more cost-effective than trading exotic pairs like the USD/TRY, which might have a spread significantly larger. Learn how to trade EUR/USD .
Figures:
A trader who makes 20 trades a day on a pair with an average spread of 1 pip will face $200 in spread costs (assuming 1 standard lot per trade), while trading a pair with a 3-pip spread would triple those costs to $600. Learn why day traders fail and how to turn it around.
Spread in 3 Different Forex Pairs
The Forex market boasts a vast array of currency pairs, each with its own characteristics. One of the most distinguishing features among them is the spread. Typically, currency pairs are categorized into 3 main groups: major pairs, minor pairs, and exotic pairs. The spread can vary significantly among pairs in these categories.
Major Pairs:
These are the most traded currency pairs in the world; they typically involve the US dollar. Examples include the EUR/USD, GBP/USD, and USD/JPY. Due to their high liquidity and trading volume, major pairs generally have the tightest spreads.
Minor Pairs:
These pairs don’t include the US dollar but involve other major currencies. Examples are EUR/GBP, EUR/AUD, and GBP/JPY. While they are still relatively liquid, their spreads are typically wider than those of major pairs.
Exotic Pairs:
Exotic pairs involve one major currency and one currency from a developing or smaller economy. Examples include the USD/TRY (US dollar/Turkish lira) and the EUR/ZAR (Euro/South African rand). These pairs tend to have the widest spreads due to lower liquidity and higher volatility.
Summary table:
Example:
On a typical trading day, a trader might observe the following spreads:
EUR/USD (Major Pair): 0.9 pips
EUR/AUD (Minor Pair): 2.3 pips
USD/TRY (Exotic Pair): 15 pips
To put things in perspective:
Trading 1 standard lot of EUR/USD with a spread of 0.9 pips costs $9.
Trading the same volume of EUR/AUD with a spread of 2.3 pips costs $23.
Trading USD/TRY with a spread of 15 pips costs a whopping $150.
The difference in spreads can significantly impact trading costs, especially for those trading in large volumes or frequently.
5 Factors Influencing the Spread
The spread in Forex trading isn’t static. It can fluctuate based on many factors, each playing a crucial role in determining how much a trader pays to enter and exit a trade. Understanding these factors can help traders plan for potential spread changes and adjust their strategies accordingly.
Market Liquidity:
Liquidity refers to the ease with which an asset can be bought or sold without causing a significant price movement. Highly liquid markets tend to have tighter spreads.
Example: Major pairs like the EUR/USD have high liquidity due to the vast number of participants trading them, leading to tighter spreads. In contrast, exotic pairs like the USD/ZAR might have wider spreads due to lower liquidity.
Time of Day (Trading Sessions):
The Forex market operates 24 hours, but not all those hours are equally active. Spreads can vary based on the trading session. Learn why forex markets are open 24 hours .
Example: The overlap of the London and New York sessions sees the highest trading volume, often resulting in tighter spreads. Conversely, the Asian session might have slightly wider spreads for certain pairs.
Economic Events and News Releases:
Major economic announcements can lead to increased volatility, which can, in turn, affect spreads.
Example: Central bank interest rate decisions, employment reports, or geopolitical events can lead to rapid price movements and wider spreads.
Broker Policies:
Different brokers have different policies and business models, which can influence the spreads they offer.
Example: Some brokers might offer fixed spreads (which stay constant), while others might offer variable spreads that can widen or narrow based on market conditions. Learn about the types of brokers.
Market Volatility:
In times of high volatility, spreads can widen as the market becomes more uncertain.
Example: Events like Brexit or unexpected election results can lead to significant market reactions and subsequently wider spreads.
3 Types of Spreads
In the Forex market, brokers offer different types of spreads to cater to the diverse needs of traders. Understanding these spread types can help traders choose the right broker and trading environment that aligns with their strategies. Learnhow to choose a broker.
Fixed Spreads:
As the name suggests, fixed spreads remain constant regardless of market conditions. They offer predictability, which is especially beneficial for traders who prefer stability in their trading costs.
Example: A broker might offer a fixed spread of 2 pips for the EUR/USD pair, meaning traders will always pay this spread regardless of market volatility or liquidity.
Variable (or Floating) Spreads:
Variable spreads fluctuate based on market conditions. They can be very tight during standard market conditions but can widen significantly during volatile times.
Example: A broker might offer a variable spread for the GBP/JPY pair that ranges from 1.5 pips during liquid times to 5 pips during major news releases.
Zero Spreads:
Some brokers offer zero spreads for certain account types or promotional periods. While the spread is zero, the broker might charge a commission per trade.
Example: A broker might offer zero spread on the USD/CAD pair but charge a $7 commission per lot traded.
Looking for Forex Brokers with Low Spreads?
At ATFX, we pride ourselves on offering competitive spreads across various currency pairs, encompassing major pairs like the EUR/USD and the GBP/USD, starting from an impressive 1.8 pips. For those familiar with MetaTrader 4 , we also provide forex trading opportunities on our hosted MetaTrader 4 platform . Start your forex trading journey with ATFX by opening a trading account today. Check out our MT4 indicators too.
From Spread Theory to Action: Explore with Our Demo Account
Understanding spreads is fundamental for any Forex trader. But, as with many things, practical experience often provides the best lessons. That’s where ATFX’s demo account comes into play.
A demo trading account allows you to trade in real-time market conditions without risking real money. It’s an invaluable tool for both novice and experienced traders, offering a sandbox environment to test strategies, understand market dynamics, and see how spreads impact trades.
Once you’re confident with your trading strategies and understanding of spreads, transitioning to a live account becomes smoother.





